Chinese companies are expanding abroad at an unprecedented pace and scale. As the number of Chinese companies going abroad has increased, so has the activity of these companies going public.
The China Securities Regulatory Commission recently updated the "Table on the Registration Status of Issuing Securities Abroad and Listing Domestic Companies (from August 1, 2024)". The table shows that a total of 120 companies have submitted registration documents to the China Securities Regulatory Commission for overseas listing, which is more than the whole of last year.
Recently, ZHU Zhenghang, a researcher in the Hundred Talents Program at the School of Management, Zhejiang University, in collaboration with Albert Tsang from the International Business School, Anhui University of Finance & Economics and SUS Tech Business School, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China, and Kun Tracy Wang from the Research School of Accounting, College of Business and Economics, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia, published their joint paper Product Market Bonding and Cross-Listings: Evidence from Global Competition Law Reforms in the top international journal Journal of International Business Studies (one of the UTD24 journals).

Click here to access the journal article
This study is dedicated to exploring the market strategy motivations of firms for cross-border listings, focusing on the impact of the institutional environment, in particular competition law reform, on firms’ listing strategies, and innovatively proposes the product-market linkage hypothesis.
The study provides a theoretical basis for understanding the cross-border activities of firms, fills the gap in the existing literature on the motives for cross-border IPOs, and helps to formulate the coordinated development of the cross-border regulatory environment and Chinese firms, thereby promoting the internationalization process.
|
ZHU Zhenghang | 朱正航 School of Management, Zhejiang University |
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
Academic Background: ZHU Zhenghang is a researcher in the Hundred Talents Program and a doctoral supervisor at the School of Management of Zhejiang University. He is mainly engaged in finance and accounting research against the background of the international capital market. His research areas include capital market supervision, corporate governance, and information disclosure. He focuses on the differences in accounting and governance standards and systems in different countries and their impact on corporate decision-making, as well as the role and dissemination of accounting information in the global capital market. You can learn more about Prof. ZHU Zhenghang’s academic background here |
|
Does Competition Policy Influence Companies Willingness of Companies to Cross-List? |

|
Image source: ©千库网 |
More and more Chinas Mainland companies with high growth and strong innovation capabilities are actively seeking overseas listings. According to the "Listing Record Status Table", these companies cover a wide range of industries, including technology, media and communications (TMT), biomedicine, autonomous driving, artificial intelligence and new consumer markets.
Existing research often suggests that the main motivation for companies to cross-list is to overcome the limitations of domestic capital markets. By gaining access to a broader international investor base, companies can improve their global market image. Cross-listing offers benefits such as expanded financing options, improved share liquidity and greater transparency in the disclosure of information.
But why are so many companies opting for cross-border IPOs at a time when global capital markets are maturing? Are these decisions driven solely by capital market factors, or do other strategic considerations also play a role?

|
Image source: ©千库网 |
In order to further explore the motivations of companies to formulate cross-listing strategies, ZHU Zhenghang together with his colleagues innovatively put forward the "product market linkage hypothesis" against the backdrop of increased competition in the domestic market in the wake of competition law reforms and examined its impact on the willingness of companies to list abroad.
The "product market linkage hypothesis" states that companies can use the characteristics of listing to strengthen their links with foreign markets through cross-listing and expand the diversity of product markets, thereby mitigating the negative impact of competition law reform on the local market. Currently, cross-listing is not only a means of financing but also an effective strategy to expand international product markets.
To test this hypothesis, researchers collected all cross-listing data from the Capital IQ Compustat database since 1990. The dataset includes 56 countries of origin of companies and 45 countries where cross-listing takes place.
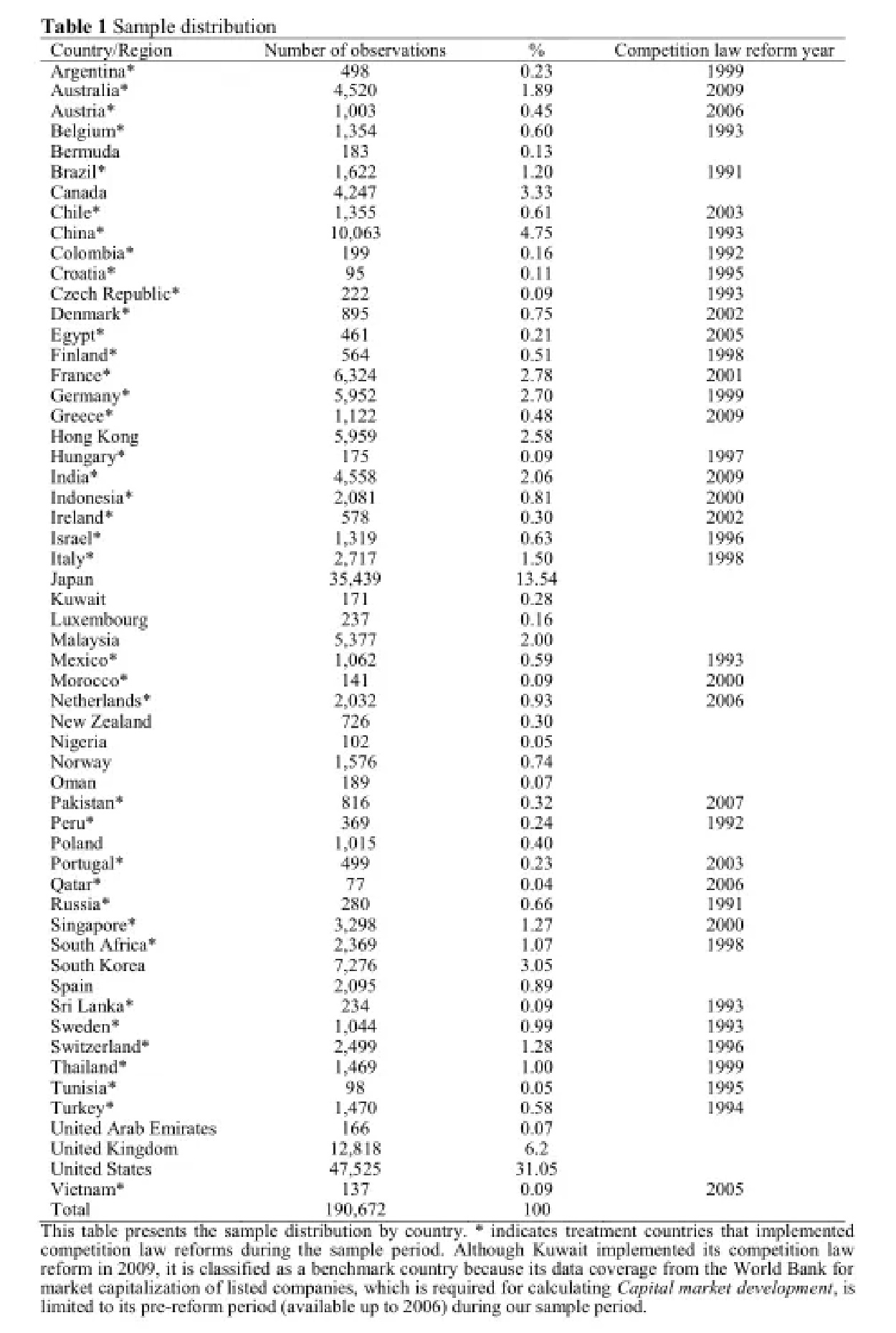
Table 1 | Sample distribution
|
After the Introduction of Competition Policy, It Is More Likely That Companies Will List Each Other |
One of the main difficulties in this study is how to test the effects of competition on the product market in a cross-national study. Since the industrial structures of the various countries are very different, it is difficult to find uniform measurement standards.
For this reason, researchers have focused on the local competition laws of enterprises in its research, assuming that the reform of local competition laws will intensify competition in the domestic market and have an impact on enterprise performance.
The team have used the comprehensive dataset and competition law index of Bradford and Chilton (2018) and Bradford et al. to identify the competition law reforms, and use a difference-in-differences design to analyze the changes in firms’ cross-listing decisions in response to shocks in the competitive environment.
The study finds that after the implementation of competition law reforms, firms are more likely to list abroad and use foreign listing as a strategic channel to establish product-market linkages through three main mechanisms: Obtaining information about customers abroad from stock prices, demonstrating a commitment to offering high quality products to foreign customers, and increasing product awareness among foreign customers.
The study’s conclusions clarify the strategic motivations for companies to go public abroad and provide actionable insights for companies to improve their market positioning in the increasingly competitive global marketplace. They help companies to formulate reasonable plans for listing abroad based on their actual conditions and the market policy environment, and to achieve sustainable development.

|
Image source: ©千库网 |
|
This Research Helps Companies to Effectively "Break Through" in The Midst of Increased Competition in the Domestic Market |
China is promoting far-reaching reforms and high-quality development by opening up at a high level. Chinese companies are also rushing to "go abroad" to maintain an effective financing environment and maximize enterprise value and equity liquidity.
This high-profile study by ZHU Zhenghang’s team has empirically proved that overseas listing improves a company’s overseas sales performance, and emphasizes that cross-listing can be an effective strategy for companies to "break through" in the context of intensified competition in the domestic market.
The study proposed and verified the "product market linkage hypothesis", which provides a new framework for understanding the motivations behind overseas listings of companies. This theory states that companies in countries with stricter competition laws are more likely to establish links to foreign product markets through overseas listings in order to avoid competitive risks.
In addition, the study shows that cross-listing allows companies to obtain important information about foreign customers, demonstrate their commitment to high-quality products and services, and improve the global visibility of their products, thereby attracting more customers abroad.

|
Image source: ©千库网 |
As companies increasingly use cross-listing as a strategic response to intensifying competition at home, it also adds momentum to the dynamic flow of global markets.
The study therefore emphasizes that attention should be paid to the wider impact that competition policy can have in order to ensure coordinated development within the cross-border regulatory framework and to encourage the development of strategic business activities while curbing anti-competitive behavior.
In addition, supportive policies are needed to encourage companies to maintain their market share of domestic products and strike a balance between promoting local economic development and entering the international market.
|
This Study Helps China’s Foreign Trade to Stabilize Its Volume and Optimize Its Structure |
Despite numerous challenges such as geopolitical conflicts and trade protectionism, global trade continues to develop. In the current international competitive landscape and volatile market environment, international and national authorities are increasingly seeking to reduce anti-competitive behavior across borders. National competition policies have far-reaching effects that not only transcend local borders, but can even change international market dynamics.
Accelerating the integrated development of domestic and foreign trade is an inherent prerequisite for building a new development pattern and promoting high-quality development. It plays an important role in promoting economic development, expanding domestic demand and stabilizing enterprises.
Cross-border listing of enterprises means restructuring of production factors, structural optimization and industrial leap. In this process, outstanding foreign enterprises can help lead high-quality and global development and promote industrial efficiency through reform and innovation.
This research helps to connect the domestic and international markets, break the traditional pattern of separation between domestic and foreign trade, and enable enterprises to flexibly coordinate the utilization of both the domestic and international markets, thereby optimizing the allocation of resources and improving the efficiency of economic activities.
At the same time, this study provides a theoretical reference for the government and regulators to strengthen supervision and policy support. It provides strategic guidance for Chinese companies’ overseas listings and helps Chinese companies to "ride the wind and waves" and sail stably in the volatile international capital markets.
|
- We would like to thank ZHU Zhenghang and Albert Tsang from Anhui University of Finance & Economics and Southern University of Science and Technology, and Kun Tracy Wang from Australian National University for sharing their exceptional research on cross-border listing strategies, which was recently published in the Journal of International Business Studies.
- You can read the original article in Chinese here