Since the introduction of ChatGPT, Generative Artificial Intelligence (referred to as "Generative AI") has quickly gained popularity among businesses and investors worldwide. Moreover, new players in the Generative AI space, such as DeepSeek, have emerged, further broadening the scope of AI-driven transformations. Consequently, Generative AI is now being implemented across various industries at an impressive pace, fundamentally changing how organizations create and how individuals work.
While Generative AI is still in its rapidly developing early stages and thus may experience technical glitches, its impressive task-processing abilities and wide-ranging application potential indicate that it is likely to transform the core responsibilities of many job roles. Additionally, it will probably change the way organizations allocate and develop human resources in the future.
This technological development poses new requirements for human resource management in the context of Generative AI applications, while also raising urgent new research questions for scholars in the field of human resource management. For example, how might the use and promotion of Generative AI change how we work? How will it influence our job content and work processes?

|
Image source: ©千库网 |
In response to the pressing need of enterprises to address new human resource management challenges in the context of Generative AI - and to further the development of organizational and management theories in the digital-intelligence era - three scholars from the Department of Leadership and Organization Management at School of Management, Zhejiang University, namely FANG Yanran, XIE Xiao-Yun, and SHI Junqi (corresponding author), have conducted in-depth research on potential new human resource management issues arising from the application of Generative AI. They approach these issues using the classic perspective of Work-Flow Analysis in human resource management.
Recently, their article was published in the 2024, Vol. 38, No. 5 issue of the journal China Science Foundation, and examines the impact of Generative AI on human resource management, synthesizes potential new human resource management issues it may bring, and forecasts future research directions in this area.

|
FANG Yanran | 房俨然 School of Management, Zhejiang University |
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
Academic Background: Hundred Talents Program Researcher, Department of Leadership and Organizational Management, School of Management, Zhejiang University You can learn more about Prof. FANG Yanran’s academic background here |
|
XIE Xiao-Yun | 谢小云 School of Management, Zhejiang University |
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
Academic Background: Professor of Leadership and Organizational Management, also Dean of the School of Management, Zhejiang University You can learn more about Prof. XIE Xiao-Yun’s academic background here |
|
SHI Junqi | 施俊琦 School of Management, Zhejiang University |
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
Academic Background: Professor of Leadership and Organizational Management, School of Management, Zhejiang University You can learn more about Prof. SHI Junqi’s academic background here |
|
Generative AI Is Already Widely Applied |
|
The following text is excerpted and organized based on the paper “Generative Artificial Intelligence and Human Resource Management Research: A Work-Flow Analysis Perspective,” authored by FANG Yanran, XIE Xiao-Yun, and SHI Junqi |
With rapidly evolving technology, Generative AI is now capable of conversing in most scenarios and on most topics almost like a real person, comprehending multimodal information, and engaging in interactions based on given contexts or human feedback. Hence, its applications in various industries have become remarkably extensive.
For instance, in the retail sector, Generative AI can help merchants craft personalized consumer experiences and predict users’ consumption interests and needs. In education and training, Generative AI can generate course content based on pre-trained data or assist with role-play, enriching both the methods and content of education and training. In healthcare, its image analysis and processing capabilities can be used for disease diagnosis and drug analysis, assisting physicians with decision-making and medical research.
Clearly, Generative AI already demonstrates exceptional capabilities in extracting, analyzing, and generating information. From the perspective of human resource management, how exactly do these capabilities function throughout the entire work process? What role does Generative AI play in the work-flow of human resource management? To discuss the potential impact of Generative AI on human resource management, we must first clarify these questions.

|
Image source: ©千库网 |
Using Work-Flow Analysis to Understand the Role of Generative AI in the Work Process
The work-flow analysis model, a specific method within job analysis, is a process organizations use to examine and confirm which critical tasks are required to produce a certain product or service. It is a key step in defining job content and requirements, allocating and developing the necessary human capital, and setting up reasonable work processes in human resource management.
Accordingly, the research team employed the Work-Flow Analysis framework in human resource management to systematically discuss the role of Generative AI in work-flow analysis.
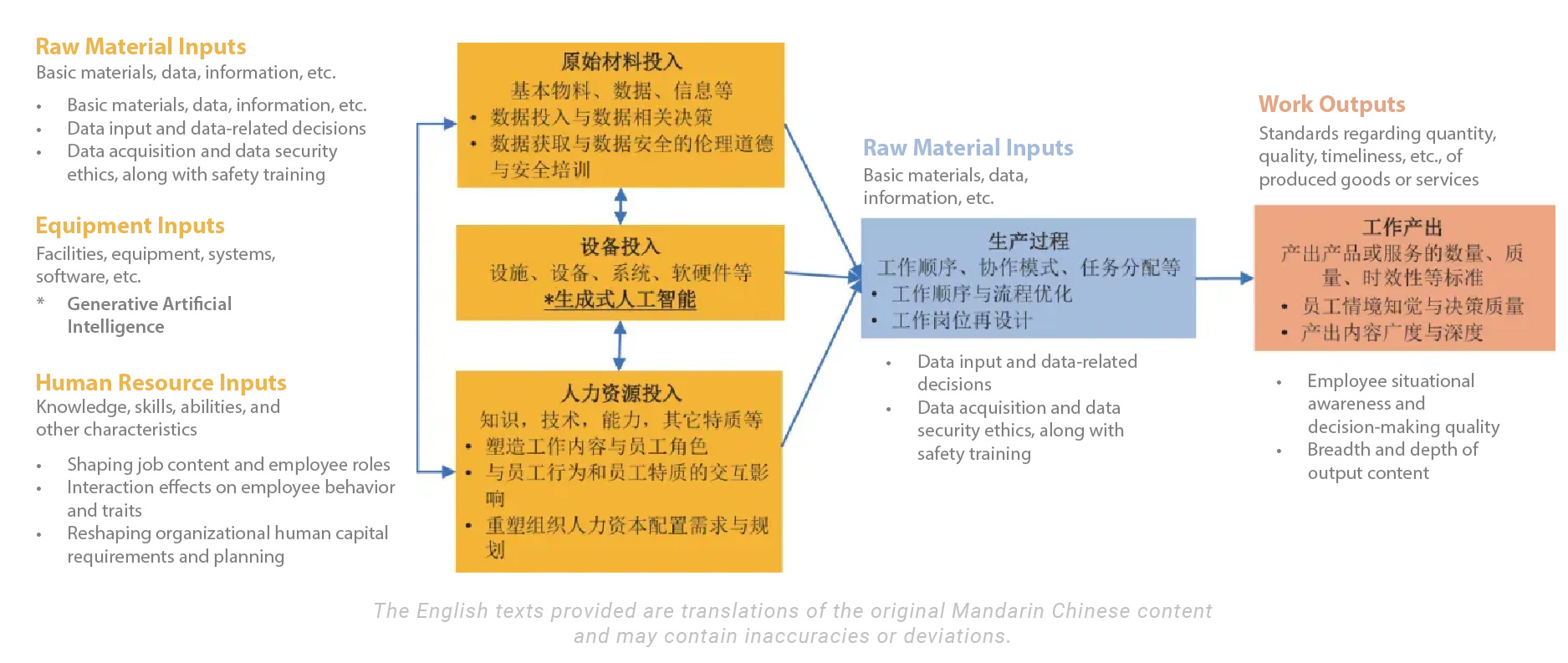
Figure 1 | Workflow analysis model and the role, potential impact and research direction of generative artificial intelligence
As shown in the basic process of work-flow analysis in Figure 1, the research team believes that, in performing a specific task aimed at producing a certain product or service, Generative AI can often be regarded as the type of “equipment” input required for output - an essential tool that helps complete particular tasks, or even a work partner for employees. It may also further influence other parts of work-flow analysis - namely, other work inputs, production processes, and work outputs.
|
Potential New Human Resource Management: Practices and Research Issues Brought about by Generative AI Applications |
From the role Generative AI plays in human resource management work-flow, it is evident that its application could lead to many changes - or even a complete reshaping - of work processes. It is therefore foreseeable that it will have a far-reaching impact on human resource management, fundamentally altering the nature of jobs, as well as employees’ work experiences and work outcomes.
But what exactly are these impacts? What new human resource management issues and challenges may emerge?
In response, drawing on the model of human resource management work-flow analysis, the research team conducted an in-depth exploration from four perspectives.
1. Impact on Raw Material Inputs: Potential Challenges in Data Decision-Making and Security Supervision
We know that to build Generative AI that is hard to imitate by competitors and that can establish corporate capabilities, organizations must train these models with massive amounts of data, and such data must be real and abundant, based on the organization or its employees. How will the data be collected? What kind of data will be collected? According to the research team, these data investment and decision-making processes may affect employees’ work perceptions and behaviors.
On the other hand, in the process of collecting, processing, or storing the data related to enterprises and individuals, ensuring privacy protection and security is a crucial issue during Generative AI’s development and application. Whether it is the leak of personal employee data or critical commercial information, the consequences can affect a company’s reputation, compliance, or even its very survival.

|
Image source: ©千库网 |
Moreover, the internal mechanisms of Generative AI systems are extremely complex, making it very difficult to monitor their data processing. This creates additional challenges in ensuring the legality and ethicality of data handling, and means that if there is data misuse or mishandling, tracing and correcting mistakes becomes more difficult and complicated.
Hence, the research team points out that Generative AI applications may also present challenges in legality, compliance, ethics, and morality. How enterprises or organizations carry out relevant human resource management measures to enhance the protection of employee and company information deserves in-depth discussion.
2. Impact on Human Resource Inputs: Potential Reshaping of Employee Experience and Human Capital Planning
“The application of Generative AI will substantially reshape what knowledge, skills, abilities, and other characteristics are in demand and how they are developed in an organization’s human capital configuration. Consequently, employees’ work roles, work experiences, and enterprises’ human resource needs and planning directions will all change accordingly,” notes the research team. These changes manifest in three specific ways:
|
01 |
Firstly, there will be changes in employees’ job content and roles. The widespread application of Generative AI alters both employees’ tasks and the requirements placed on employees. In turn, organizations’ needs and allocations for human capital also change accordingly. Moreover, Generative AI applications can lead to two distinct outcomes: it can completely replace human employees or assist them in completing tasks. The former can improve employees’ work experiences, while the latter may threaten employees’ professional identity and professional value, eroding their sense of meaning at work and increasing job insecurity—thus creating new challenges for human resource management. |
|
02 |
Secondly, there will be changes in employees’ interactive behaviors and work experiences. When Generative AI is embedded in the work process, employees need to interact not only with other people but also with the AI. Their attitudes toward Generative AI and how they interact with it will directly influence the effectiveness of Generative AI use, and thus the effectiveness of human resource management in the context of Generative AI. Consequently, exploring the optimal alignment and interaction configurations among employees’ personal knowledge, abilities, skills, and other characteristics with Generative AI—and the outcomes of such configurations—will be an important topic in future human resource theory and practice. |
|
03 |
Finally, there will be changes in organizational-level human capital requirements and planning. When Generative AI can produce acceptable-quality content much faster, to some extent it lowers the threshold for certain tasks. Hence, for enterprises and organizations, the questions of reskilling and upskilling employees in a Generative AI environment, how best to match and pair Generative AI with employees—along with the processes, outcomes, and boundary conditions of these pairings—are all urgent research topics. At the same time, enterprises and organizations must redefine existing job positions and job descriptions based on specific Generative AI applications, updatethe requirements and methods for recruitment, training, and performance evaluation, and reconsider the configuration and planning of human capital. |
3. Impact on the Production Process: Potential New Challenges in Employee Management and Job Design
According to the research team, Generative AI may also reshape the specific processes of work output, including employees’ sequences and workflows, as well as the design of jobs at the organizational level. This creates new challenges and requirements for how enterprises select, train, and develop employees, and how they design jobs and manage employees.
For example, in the process of completing tasks, depending on the organizational design, the nature of the tasks, and employees’ personal characteristics, AI may intervene at different stages of the process through various human–machine collaboration models: fully automated, sequential, interactive, etc. Each of these approaches will directly influence the depth and breadth of the solutions generated. In turn, this will impact the process and quality of task completion, employees’ work experiences, and the effectiveness of both employees and the organization.

|
Image source: ©千库网 |
Similarly, when introducing Generative AI into work processes, enterprises and organizations often need to consider how safe, reliable, and practically applicable the AI’s information processing, analysis, and output are. That is, they must ensure that employees in AI-assisted scenarios have sufficient situational awareness to complete tasks successfully. This scrutiny, supervision, and decision-making process becomes more dependent on employees’ knowledge, skills, abilities, and experiences related to the tasks at hand. It requires professionals well-versed in both the external and internal environment of the organization to reassess and reprocess the content generated by AI.
In addition, enterprises and organizations must think about which tasks can be handed over to Generative AI and which still require human employees. They also need to anticipate the impact on employees’ work experiences, attitudes, and behaviors when employees’ judgment diverges from AI’s judgment. Accordingly, enterprises and organizations should consider and adjust how heavily they rely on and utilize Generative AI for different types of tasks.
4. Impact on Work Outputs: Potential Impact on Decision-Making Quality and Output Quality
Regarding work outputs, the research team indicates that enterprises or organizations outfitted with Generative AI will also redefine the needs for the products or services they produce - thus introducing new requirements for supervising and evaluating decision quality and output quality at both the employee and organizational levels.
Specifically, in terms of decision-making quality, how much situational awareness (i.e., the ability to perceive and understand key elements in one’s environment at a specific time and space, comprehend their meanings, and predict their future states) employees can retain while collaborating with AI—and how important that awareness is to the tasks at hand - will influence the quality of decisions made with AI assistance. At the same time, decisions based on Generative AI’s output may be biased due to inherent biases in the data used in its pre-trained models.

|
Image source: ©千库网 |
Regarding output quality, Generative AI can help people obtain and process large amounts of task-relevant information more efficiently, resulting in more comprehensive, diverse outcomes. However, because Generative AI’s output relies on learned data and information, the outcomes may lack depth and specificity, thereby constraining the diversity of newly generated content. This can significantly affect the quality of employees’ and organizations’ outputs.
Given these potential drawbacks, the research team emphasizes that to fully harness Generative AI, organizations and employees must deepen their understanding of the fundamental principles and training methods of these technologies. They must also fully account for the organization’s internal and external environment, the core characteristics of its human resources, and the nature of its tasks, achieving a thorough coupling of Generative AI, task features, human resources, and the organization’s strategic objectives.
|
Conducting Multi-Disciplinary Research with Generative AI May Be the Key to “Solving the Puzzle” |
Generative AI, as a rapidly evolving and disruptive technology, not only brings new issues and challenges to the practice of human resource management in enterprises and organizations but also affects human resource management research itself in a variety of ways.
According to the research team, as Generative AI represented by ChatGPT can perform at near-human levels in textual comprehension and processing, often at a low cost, employing such AI as a new method in human resource management research is a possible way forward. Although its reliability and robustness require further empirical validation, Generative AI’s potential application in research could allow preliminary explorations and hypothesis testing without directly involving human participants.
Furthermore, as technology advances - especially with Generative AI such as ChatGPT’s extensive use in enterprises and organizations - the field of human resource management faces unprecedented challenges and opportunities. These challenges and opportunities involve not just traditional human resource management knowledge and practice but also intersect with computer science, data science, ethics, law, psychology, and more. Thus, to fully understand and effectively respond to the new challenges Generative AI poses for human resource management, it is urgent to conduct multi-disciplinary and cross-domain research. This will lead to a deeper understanding of AI’s potential and challenges, helping to develop more efficient and responsible human resource management strategies and practices.

|
Image source: ©千库网 |
The research team concludes that it is vital to explore how the application and adoption of Generative AI actually influence the nature of jobs in various industries, how they shape the demands on employees in different roles, and what organizational environments are required to support this transformation. These questions need to be examined more deeply at the work, individual-employee, team-and-department, and even organizational levels within human resource management.
Although truly ‘generative’ AI is still evolving, and its application in enterprises and organizations is not yet as ubiquitous as other information or digital technologies (and its profound impact on job content, employees’ work experiences and career development, and employment relationships between employees and organizations has not fully materialized) in light of the rapidly advancing Generative AI trend, there is still a pressing need to conduct targeted empirical research. Through multi-disciplinary and cross-domain approaches that deeply investigate the technological characteristics of Generative AI and its application contexts, such research can yield concrete, relevant findings.
- Progress in human resource management theory and practice influences the cultivation and development of new productivity in enterprises and organizations, as well as the construction of modern industrial systems. We thank our researchers for their contributions to the industry!
- You can read the original article in Chinese here